LIAI Committee Report
If you have any questions or comments regarding the accessibility of this publication, please contact us at accessible@parl.gc.ca.
Appendix A: Virtual Committees Dashboard (February to June 2022)
Figure 1–Pre-tests for witnesses appearing by videoconference (by percentage and number of witnesses)
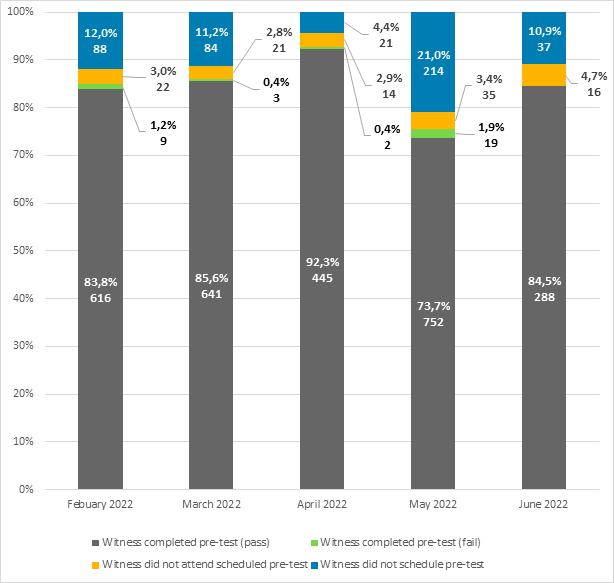
Since February 2021, the House Administration calls all committee witnesses to schedule pre-tests.
Figure 2–Source of headset with microphone used by witnesses appearing by videoconference (by percentage of witnesses)
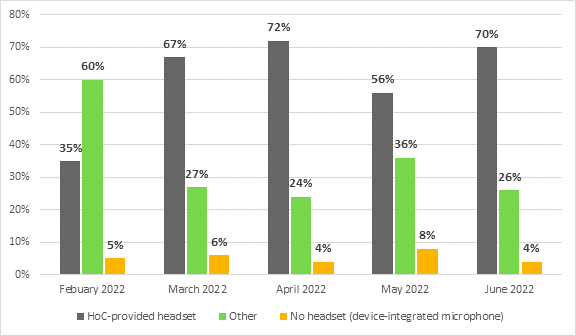
Figure 3–Witnesses appearing by videoconference with audio-quality issues recorded during committee meetings (by percentage and number of witnesses)
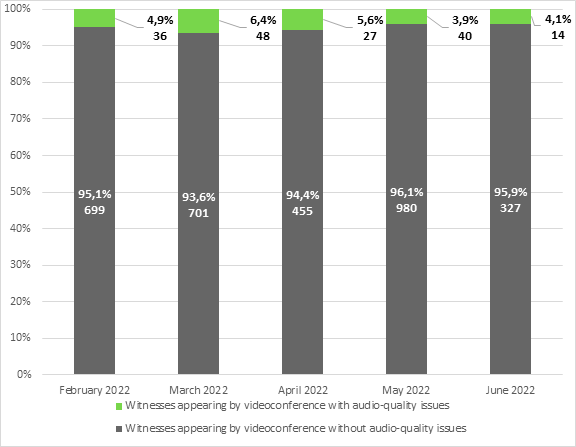
Figure 4–Causes of audio-quality issues experienced during committee meetings by witnesses appearing by videoconference (by number of recorded issues and resolution)
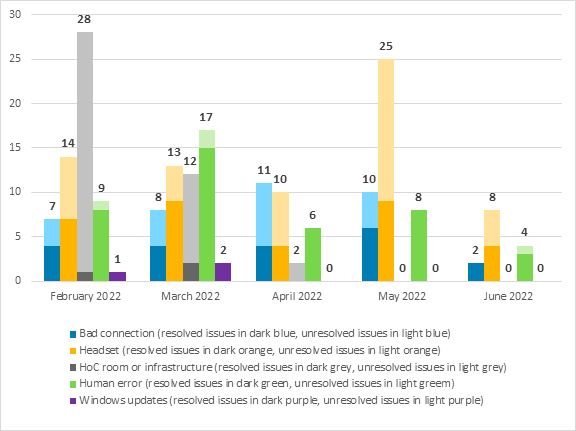
Issues that could affect a witness' ability to participate in the meeting continue to be identified and, where possible, resolved, during the pre-test and the verification immediately prior to the meeting.
Table 1–Issues experienced by witnesses during pre-test and verification immediately prior to committee meeting
Month |
Number of Issues |
Issues Resolved (%) |
February 2022 |
171 |
96% |
March 2022 |
95 |
98% |
April 2022 |
74 |
96% |
May 2022 |
74 |
94% |
June 2022 |
72 |
82% |
Figure 5–Network connection of committee meeting participants (by percentage of participants)
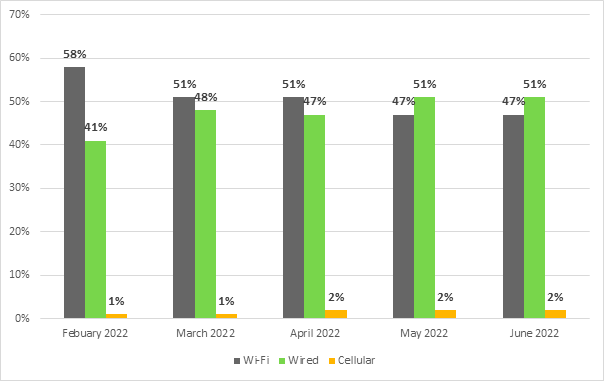
In general, wired connectivity provides a better audio chain.